
For a complete diagram of body fluid compartments, see body fluid compartments of a 70-kg man and body fluid compartments of a 55-kg woman. So whenever were talking about fluid compartments, we are pretty much looking at three primary fluid compartments, and Im gonna break these down a little bit.

Note that this diagram places focus only on these three major fluid compartments. The human body has strict physiologic control to maintain a balance of fluid and electrolytes. The TBW varies with age 70 in infants, 65 in children, and 60 in adults. Two-thirds of the total body water (TBW) is intracellular. Plasma is the smallest fluid compartment (~8% of total body water). There are two major fluid compartments: the intracellular fluid (ICF) and the extracellular fluid (ECF). Figure 26.1.2 Fluid Compartments in the Human Body: The intracellular fluid (ICF) is the fluid within cells. Interstitial fluid contains ~25% of the total body water. Extracellular fluid has two primary constituents: the fluid component of the blood (called plasma) and the interstitial fluid (IF) that surrounds all cells not in the blood (Figure 26.1.2). The intracellular fluid compartment contains most of the water in the body (~67% of total). The right diagram shows the three major fluid compartments drawn to scale. The left diagram allows for a better demonstration of the relationship between the intracellular fluid, interstitial fluid, and plasma, however, the relative size of each of the compartment is not drawn to scale. Waste products produced by cells follow the reverse path from the cytoplasmic compartment to plasma. The intracellular compartment is the space within the organisms cells it. They then must cross the plasma membrane to enter the cytoplasmic compartment of cells. The two main fluid compartments are the intracellular and extracellular compartments. Nutrient molecules traveling in the blood must first cross the capillary endothelium to enter the interstitial fluid. The capillary endothelium is the physical barrier that separates the interstitial fluid from plasma. The physical barrier separating the intracellular fluid compartment (i.e., cytoplasm) and the interstitial fluid is the cell plasma membrane. Fluid, molecules, and ions flow across physical barriers between the fluid compartments. These are the (1) intracellular fluid compartment, (2) interstitial fluid, and (3) plasma.

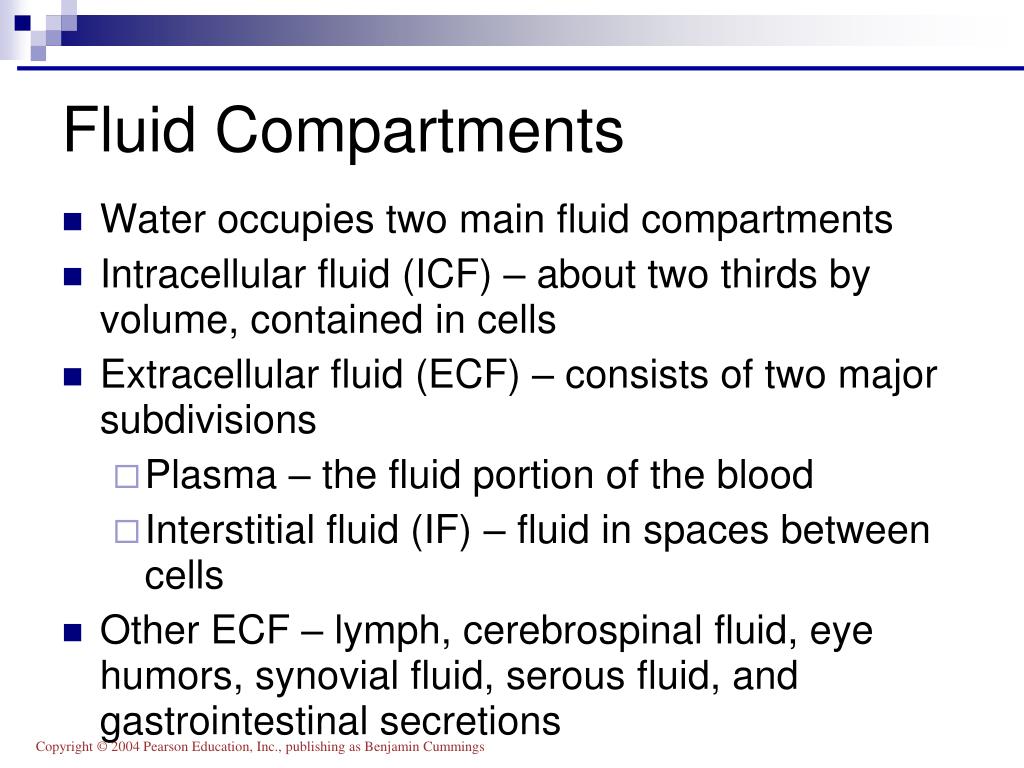
In which compartment of the body is the majority of water stored The intracellular fluid (ICF. The extracellular fluid is the body fluid located outside the cell(s). In the human body plan, there are three major fluid compartments that are functionally interconnected. How many fluids are in the human body In humans, the body fluid can be classified into two major types according to location: (1) intracellular fluid and (2) extracellular fluid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
